Bioelectrography and Surgery
For several years research project for evaluation of patients’ condition after surgery was conducted in Saint Petersburg Military Medical Academy. A lot of papers were published in Russian medical journals and two PhD in medicine were awarded.
Two papers were published in English [Polushin et.al. 2004, 2009]. The main conclusions were as follows:
1. There are reliable differences between parameters of GDV-grams of practically healthy people and patients with chronic abdominal surgical pathology.
2. The data obtained indicate that GDI parameters are connected with the functional status of the organism and reflect the severity of the somatic state of patients with abdominal surgical pathology.
3. The most informative parameters are: “integral area of glow JS” in the “GDV Diagram” program; “total” and “normalized area”, “total density”, “average brightness”, as well as “fractality” and “form coefficient” in the “GDV Processor” program.
4. The most informative mode of registration of GDV-grams is the mode “without filter”. On the whole, the application of the filter keeps the trend of changes, but they are often less pronounced and lose statistical significance.
5. The revealed variability of GDV-gram parameters depending on the sex and age of patients indicates that it is necessary to determine their individual norms.
6. The dependence of perioperative dynamics of a number of indices on the severity of the patient’s somatic state, the patient’s age and the duration of surgical procedure enables functional monitoring in the postoperative period, and evaluation of operative stress.
7. The parameters of EPI-grams reliably change in response to the operative trauma, and their dynamics depend on the severity of the somatic state of patient, which allows using the technique for functional monitoring of patients in postoperative period, as well as for the assessment of the operative stress. The degree of intensity of changes depended on the volume and character of the undergone physical intervention. Thus, patients who had laparoscopic cholecystectomy showed much smaller changes of bioenergy status in comparison with patients, who had stomach and intestine’s operations.
8. The Electrophotonic Imaging technique is mostly advisable for the dynamic assessment of the functional state of patient in perioperative period. Not all the fingers may be used, at that, but only one finger of each hand. For example, the fourth finger, where the changes are the most significant.
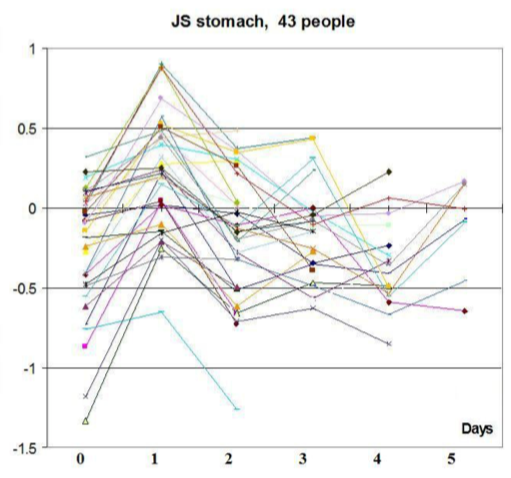
Fig. . Dynamics of some GDV indices in perioperative period. Stages of research: 1- before surgery, 2 – 1st hour after surgery, 3 – in 1 day after surgery, 4 – in 2 days after surgery, 5 – in 3 days after surgery, 6 – in 4 days after surgery, 7 – in 5 days after surgery.
Dynamics of GDV-gram parameters of systems in perioperative period for 43 people. (0 – before surgery, 1 – first hour after surgery, 2-5 days after surgery).
Important approach for monitoring of
GDV parameters to predict the development of postoperative delirium was developed by Strukov EU. and Tuzhikova N.V. [2010].
122 people were surveyed using prospective a GDV technique.
Electrophotonic Analysis in Medicine Bioelectrography and Surgery
Bioelectrography and Surgery GDV technique
Three groups were examined.
The first (control) were 47 healthy people surveyed by GDV against the background of psycho- emotional well-being.
The second group included 50 patients operated on the abdominal organs. GDV-grams were recorded in the group before surgery and during the next five days postoperatively.
The third group consisted of 25 patients treated at the clinic of psychiatry with the abstinent syndrome in pre-and delirious state.
The most informative was glow area parameter. In series taken in dynamics the most significant changes were revealed. Dynamics of the glow area parameter of patients, whose postoperative period is complicated by the development of delirium, is different from the normal distribution and was characterized by high amplitude of the GDV area. Dynamic changes in the glow area were similar to the dynamics of GDV images of patients with psychiatric profile.
However, these changes in the operated patients may be revealed 10-12 hours prior to the development of the clinical picture of delirium. As the delirious syndrome subsided, the parameter of GDV area comes back to the original data and fits into the standard distribution. Such performance of dynamics of the GDV area and its fundamental similarity to that of patients with psychiatric profile allows us to speak with confidence about the possibility of prognosis of delirious syndrome in patients operated on the abdominal organs in the immediate postoperative period, even before the development of complications.
